AI Video Accessibility India 2026: Deliver WCAG- and RPD-Compliant, Deaf-Friendly Video at Enterprise Scale
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- India’s 2026 landscape demands WCAG 2.2, GIGW 3.0, and RPD Act compliance for video accessibility across public and private sectors.
- High-quality accessibility hinges on accurate captions (≤ 5% WER), ISL integration, and culturally aware, multilingual workflows.
- Agentic AI enables scalable, localized solutions—from captioning and ISL avatars to compliance audits—suited to India’s “Hinglish” and regional contexts.
- Enterprises can achieve measurable ROI through market expansion, SEO gains, and legal risk reduction via accessibility-first production.
- Platforms like Studio by Truefan AI streamline end-to-end accessible video creation with captions, ISL avatars, and governance.
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape of the subcontinent, AI video accessibility India 2026 has transitioned from a niche corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiative to a fundamental legal and strategic requirement. As India’s internet user base is projected to surpass 900 million by 2026, with video content accounting for a staggering 82% of all mobile data traffic, the imperative to reach the estimated 63 million Indians living with significant auditory impairment has never been more urgent. For enterprises, government bodies, and educational institutions, achieving “accessibility-first” video production is no longer just about compliance; it is about unlocking a massive, underserved market through inclusive design.
The convergence of agentic AI and context-aware systems in 2026 is finally providing the tools necessary to bridge the communication gap. Platforms like Studio by Truefan AI enable organizations to generate high-fidelity, localized video content that integrates these accessibility features from the ground up, ensuring that every viewer—regardless of their hearing ability—can perceive, understand, and interact with digital media.
1. The Regulatory Landscape: RPD Act, GIGW 3.0, and WCAG 2.2
Navigating the legal requirements for video accessibility in India requires a multi-layered understanding of domestic laws and international standards. By 2026, the enforcement of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPD) Act 2016 has matured, with stricter oversight on digital service providers to ensure non-discrimination in information access.
The RPD Act 2016 and Digital Mandates
The RPD Act 2016 explicitly mandates that all “information and communication” must be accessible. For the video medium, this translates to a requirement for RPD Act compliant videos AI solutions that provide equivalent alternatives for audio information. Failure to comply is increasingly resulting in legal audits for public-facing enterprises, particularly those in banking, healthcare, and education.
GIGW 3.0: The Gold Standard for Government Portals
The Guidelines for Indian Government Websites (GIGW) 3.0, launched to modernize India's digital infrastructure, aligns closely with the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG). For any entity working with the public sector, GIGW 3.0 compliance is non-negotiable. Key features include:
- Mandatory Captions: All pre-recorded and live video must have synchronized captions.
- Sign Language Integration: High-impact public service announcements must include Indian Sign Language (ISL) interpretation.
- Accessible Players: Video players must be keyboard-navigable and compatible with screen readers.
WCAG 2.2 Mapping for Indian Video
To achieve WCAG compliant video India status, content must meet the 2.2 standards, specifically focusing on:
- Success Criterion 1.2.2 (Captions - Prerecorded): Captions are provided for all prerecorded audio content in synchronized media.
- Success Criterion 1.2.4 (Captions - Live): Real-time captions for live broadcasts.
- Success Criterion 1.2.6 (Sign Language - Prerecorded): Providing ISL for content that is critical for rights, safety, or benefits.
Source: DigitalA11Y - Digital Accessibility Laws in India; GIGW 3.0 Introduction
2. Precision Captions: Metrics, WER, and AI-Driven Accuracy
In 2026, auto-captions are no longer sufficient for enterprise-grade accessibility. The focus has shifted to closed caption accuracy AI tools that can handle the linguistic complexity of the Indian market, including “Hinglish” and regional code-switching.
Measuring Success: Word Error Rate (WER)
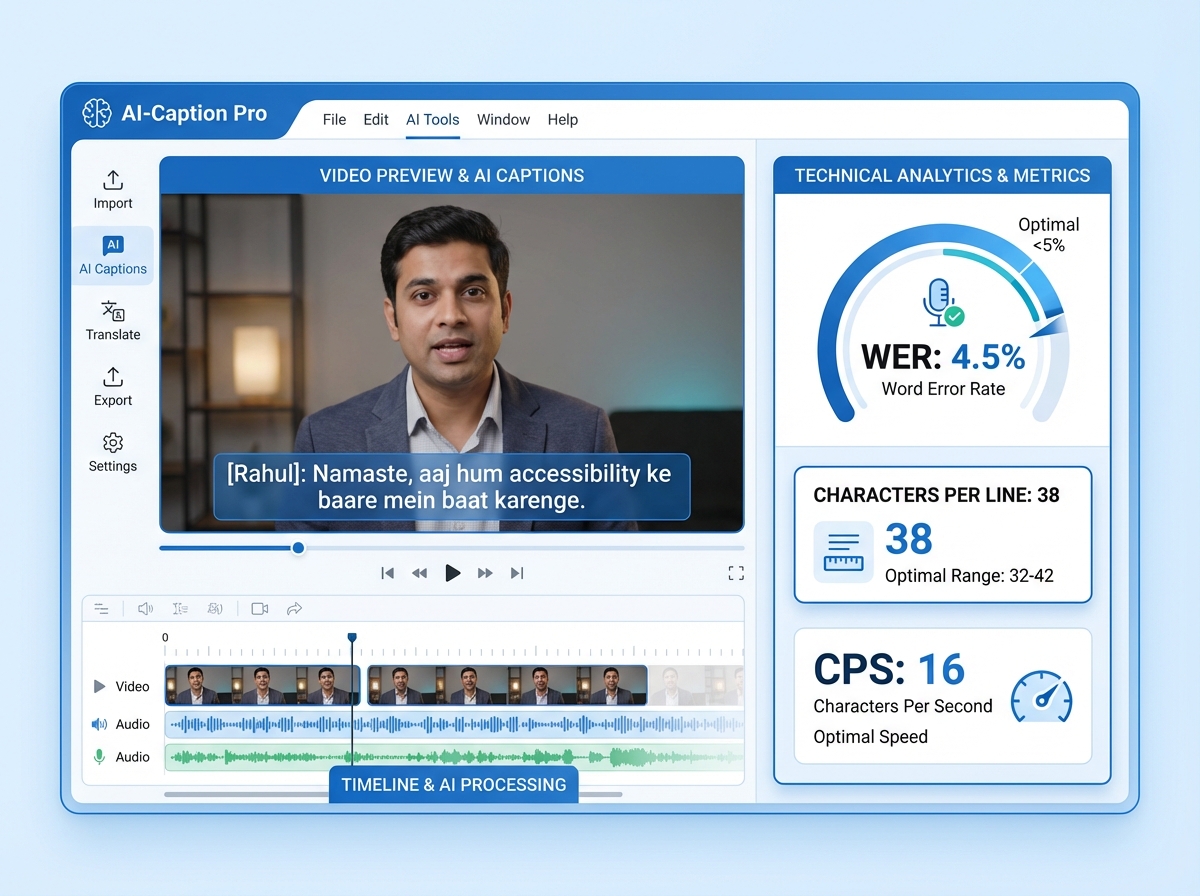
The primary metric for hearing impaired video captions AI is the Word Error Rate (WER).
- The Formula: WER = (Substitutions + Deletions + Insertions) / Total Words.
- The 2026 Benchmark: For deaf-friendly video content AI, enterprises should aim for a WER of ≤ 5% after human-in-the-loop (HITL) verification.
Technical Standards for Readability
To ensure AI subtitles deaf community India are actually usable, they must adhere to strict readability guidelines:
- Characters Per Line (CPL): Maximum 42 characters to prevent visual fatigue.
- Characters Per Second (CPS): 15–20 CPS is the “sweet spot” for comfortable reading speeds.
- Diarization: AI tools must accurately detect speaker changes and label them (e.g., [Rahul]: “Hello”) to provide context in multi-person dialogues.
- Non-Speech Information: Brackets must be used for meaningful sounds like [upbeat sitar music] or [door slams] to provide a full sensory experience.
Solving the “Hinglish” Challenge
India’s unique linguistic landscape requires AI models that understand context. Agentic AI systems in 2026 use “context engineering” to reduce hallucinations in captions. For example, an AI must distinguish between “koshish” (effort) and “courses” based on the surrounding technical or conversational context. Studio by Truefan AI’s 175+ language support and AI avatars leverage these advanced NLP models to ensure that regional nuances are preserved, not erased.
Source: EY India - Is India Ready for Agentic AI? Outlook 2026
3. ISL Integration: Avatars, Grammar, and Cultural Nuance
While captions are vital, they are often a second language for many in the deaf community whose primary mode of communication is Indian Sign Language (ISL). The rise of the ISL Indian Sign Language avatar represents the frontier of sign language video integration AI.
ISL Grammar vs. Literal Translation
A common mistake in inclusive content creation AI is attempting a word-for-word translation from English/Hindi to ISL. ISL has its own distinct syntax and grammar.
- Topic-Comment Structure: ISL often places the subject first, followed by the action or description.
- Non-Manual Markers (NMMs): Facial expressions and body tilts are grammatical features in ISL, not just emotional expressions. An AI avatar must accurately render these NMMs to be understood.
The Role of AI Avatars in 2026
By 2026, high-fidelity AI avatars have become the preferred method for scaling ISL. Unlike human interpreters who may not be available 24/7 for every piece of content, an ISL Indian Sign Language avatar can be generated alongside the primary video.
- Semantic Accuracy: 2026 models achieve ≥ 95% semantic accuracy by using ISL glossing—a system of writing signs to ensure the AI understands the linguistic structure before rendering.
- Bandwidth Optimization: In India, where mobile data can be inconsistent, AI-generated ISL overlays are often delivered as lightweight vector-based streams, ensuring accessibility even on 3G/4G networks.
Source: IndiaAI - How AI could help you learn sign language; Indic AI - Disability to Distinction with AI
4. The Tech Stack: Tools and Workflows for Inclusive Video
Building an accessibility-first video production workflow requires a specialized stack of hearing accessibility video tools. In 2026, the most successful teams use an integrated approach that combines creation, captioning, and compliance auditing.
The End-to-End Workflow
- Pre-Production: Use AI to analyze scripts for “caption-friendliness.” Avoid overly complex jargon and mark segments where ISL interpretation will be critical.
- Production: Ensure the visual frame includes a “safe zone” for the ISL avatar or caption box. Clean audio recording is essential for minimizing WER in the next stage.
- Post-Production:
- AI Captioning: Generate timestamped .srt or .vtt files.
- ISL Overlay: Integrate the sign language track.
- Human QA: A deaf or hard-of-hearing reviewer performs a final check on timing and cultural nuance.
- Distribution: Use accessible video creation tools India to publish to platforms like YouTube, ensuring that “Closed Captions” are toggled ON by default for specific audience segments.
Accessible YouTube Content India
For creators targeting the Indian market, accessible YouTube content India strategies involve more than just uploading a video. It includes:
- Multilingual Captions: Providing tracks in Hindi, English, and at least one regional language (e.g., Tamil, Telugu, or Bengali).
- Descriptive Transcripts: Providing a full text-based version of the video in the description for screen-reader users.
- Chapter Markers: Using AI to auto-generate chapters, allowing users to navigate to specific sections easily.
Source: PIB - World Hearing Day: 63 Million Indians Affected

5. Enterprise Governance: Scaling Accessibility with ROI
For large organizations, accessibility is a governance challenge. Solutions like Studio by Truefan AI demonstrate ROI through reduced legal risk, expanded market reach, and enhanced brand reputation. In 2026, the “Business Case for Accessibility” is backed by hard data.
The ROI of Inclusion
- Market Expansion: Tapping into the 63M+ deaf/HoH population increases potential viewership by nearly 7% in India.
- SEO Benefits: Search engines index video transcripts and captions. AI video accessibility India 2026 strategies directly improve organic search rankings.
- Retention: Studies in 2026 show that 80% of all viewers (including those with full hearing) are more likely to finish a video if captions are available, especially in “sound-off” environments like public transport.
Governance and Compliance Audits
Enterprise-scale accessibility requires a centralized dashboard to track compliance across thousands of assets.
- ISO 27001 & SOC 2: Ensure your AI providers meet global security standards.
- Audit Logs: Maintain records of caption accuracy checks and ISL linguistic reviews for RPD Act audits.
- Moderation: Use real-time filters to ensure that AI-generated captions or avatars do not produce hallucinated or inappropriate content.
Source: ET CIO - 2026 AI Trends: India’s Journey Towards Integration
6. The 2026 Roadmap: A Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
As we look toward the end of 2026, the roadmap for AI video accessibility India 2026 is clear. Organizations must move from reactive “bolted-on” accessibility to proactive “built-in” inclusion.
Phase 1: The Accessibility Audit (Months 1-2)
- Evaluate existing video libraries for WCAG 2.2 compliance.
- Identify “High-Impact” videos (e.g., HR policies, safety training, product launches) for immediate remediation.
Phase 2: Tooling Integration (Months 3-4)
- Adopt disability inclusion video AI tools that support ISL and regional languages.
- Establish a “Glossary of Terms” for the AI to ensure brand-specific jargon is captioned correctly every time.
Phase 3: Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Training (Months 5-6)
- Train internal DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion) teams to use AI editors for rapid caption correction.
- Partner with ISL experts to validate avatar performance.
Phase 4: Continuous Monitoring (Ongoing)
- Implement automated QA dashboards to track WER and CPS across all new content.
- Collect feedback from the deaf and hard-of-hearing community to iterate on avatar fidelity and caption placement.
Summary of 2026 Data Points:
- 63 Million: Number of Indians with significant auditory impairment (PIB).
- $17 Billion: Projected size of India's AI market by 2027 (NASSCOM/EY).
- 82%: Percentage of internet traffic attributed to video in 2026.
- 900 Million: Projected number of internet users in India by 2026.
- 22.26%: The ROI of high-quality, accessible blog and video content in 2026 (HubSpot).
- 48.7%: Projected usage of voice and assistive AI interfaces among Indian smartphone users (eMarketer).
Conclusion
By integrating rigorous WCAG 2.2 and GIGW 3.0 practices with AI-driven captioning, ISL avatars, and enterprise governance, Indian organizations can make video truly inclusive—while unlocking measurable business value. Precision metrics like WER and CPS, combined with culturally aware NLP for “Hinglish” and regional languages, ensure content is both compliant and comprehensible.
To operationalize accessibility at scale, teams can leverage platforms such as Studio by Truefan AI to create, localize, and audit accessible video content across thousands of assets—delivering a consistent, deaf-friendly experience across India’s diverse digital audience.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes a video “WCAG compliant” in India for 2026?
To be WCAG compliant video India ready, your content must meet the 2.2 Level AA standards. This includes providing accurate captions (Success Criterion 1.2.2), audio descriptions for visual-only information (1.2.5), and ensuring the video player is fully operable via keyboard (2.1.1). In the Indian context, aligning with GIGW 3.0 is also essential for any public-sector engagement.
How do I measure the accuracy of AI-generated captions for the deaf community?
You should use closed caption accuracy AI tools that provide a Word Error Rate (WER) report. For the AI subtitles deaf community India relies on, a WER of less than 5% is the gold standard. Additionally, you must monitor the “Characters Per Second” (CPS) to ensure the text doesn’t move too fast for the average reader.
When should I use an ISL Indian Sign Language avatar instead of just captions?
While captions are essential for many, an ISL Indian Sign Language avatar is critical for users whose first language is ISL. You should prioritize ISL for safety-critical information, government announcements, and educational content where nuance and emotional tone—conveyed through signs and facial expressions—are vital for full comprehension.
Can AI tools handle “Hinglish” and regional Indian dialects for captions?
Yes, modern hearing accessibility video tools in 2026 use advanced NLP models trained on Indic datasets. These tools can recognize code-switching (mixing Hindi and English) and provide accurate, timestamped captions that reflect how people actually speak in India.
How does Studio by Truefan AI help with video accessibility?
Studio by Truefan AI’s 175+ language support and AI avatars allow teams to generate accessible content rapidly. The platform includes an in-browser editor specifically designed to trim timing, add precise captions, and export videos in multiple aspect ratios, making it one of the most versatile accessible video creation tools India has to offer for enterprises looking to scale their DEI efforts.
Is the RPD Act 2016 applicable to private companies’ video content?
Yes. While the RPD Act 2016 initially focused on government services, the interpretation has expanded. Private entities providing “public services” (including digital news, banking, and e-commerce) are increasingly expected to provide RPD Act compliant videos AI to ensure they do not exclude citizens with disabilities.




