Enterprise video batch processing 1000 daily: MLOps + CI/CD playbook for India-focused growth teams
Estimated reading time: 11 minutes
Key Takeaways
- Achieving 1,000+ daily renders requires a distributed orchestration layer, GPU autoscaling, and resilient job queues.
- MLOps discipline (model registries, canary rollouts, safety gates) is essential for reliable avatar, TTS, and lip-sync pipelines.
- CI/CD for video treats templates as code with automated visual, audio, and subtitle regression tests.
- India-first compliance (DPDP), vernacular support, and bitrate ladders optimize reach and minimize risk.
- Cost optimization via caching, spot instances, and throughput planning protects unit economics at scale.
For performance marketers and growth engineers, enterprise video batch processing 1000 daily is now achievable with standardized templates, parallel video rendering systems, and production-grade MLOps video production infrastructure. In the 2026 digital landscape, where India’s GenAI video market is projected to grow at a 48% CAGR, the ability to generate hyper-personalized content at industrial scale is no longer a luxury—it is a competitive moat.
This playbook defines the architecture, operational discipline, and compliance frameworks required to build a high-volume video generation workflow. Whether you are scaling a D2C brand across Tier 2 cities or managing a fintech’s vernacular outreach, the shift from “creative-first” to “infrastructure-first” video production is the key to unlocking sustainable ROI. Platforms like Studio by TrueFan AI enable growth teams to bridge this gap by providing the underlying API-driven infrastructure needed for such massive throughput.
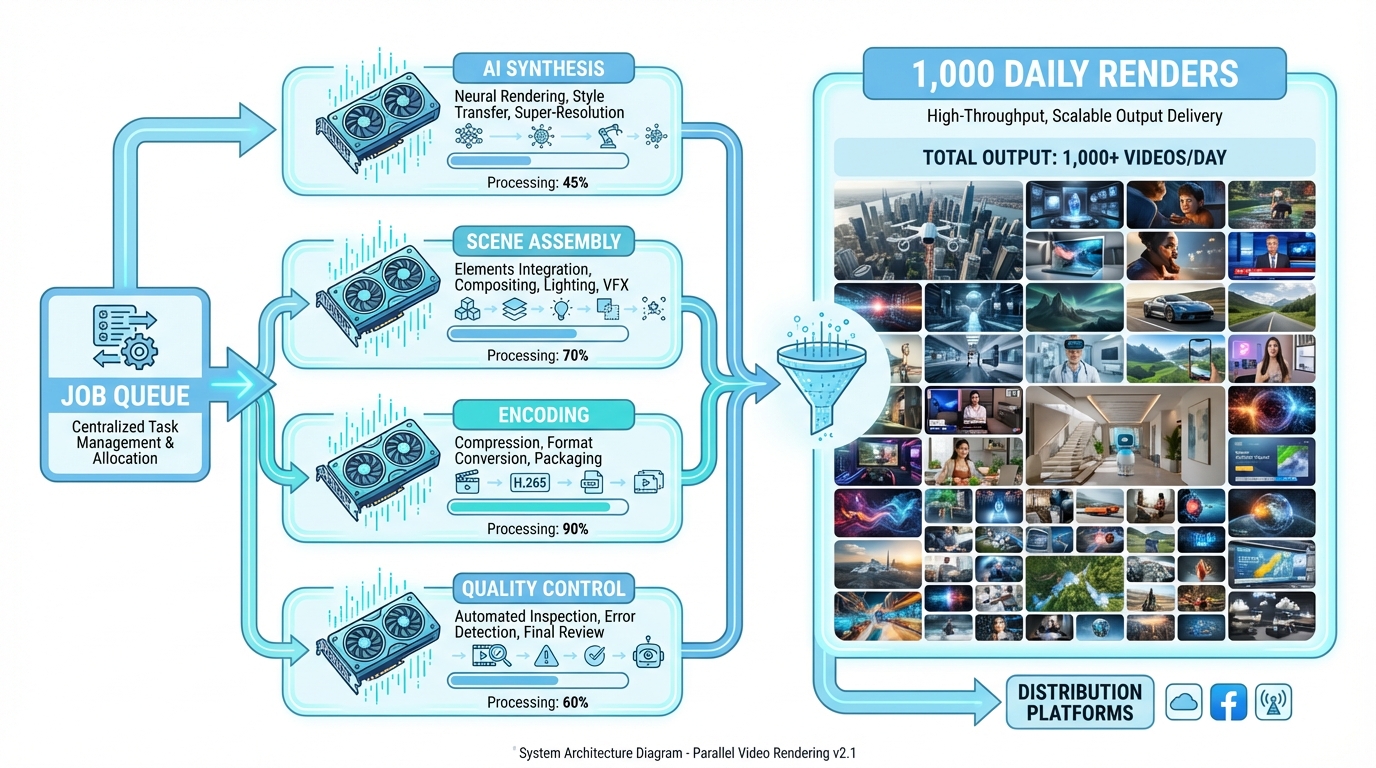
1. The Reference Architecture for 1,000+ Daily Renders
Building an enterprise batch video infrastructure capable of handling 1,000+ daily renders requires moving away from monolithic rendering and toward a distributed, microservices-based approach. The core of this system is an orchestration layer that manages job queues and resource allocation; see this reference on video production infrastructure.
Orchestration and Job Queues
To manage enterprise video batch processing 1000 daily, you must implement workflow engines like Argo Workflows or Kubeflow. These engines handle per-job metadata, including template IDs, personalization variables (name, offer, locale), and target channel specifications. A robust queue system (e.g., RabbitMQ or Kafka) ensures that high-priority “hot” campaigns can pre-empt lower-priority background tasks, maintaining strict SLAs for time-sensitive marketing pushes.
Parallel Video Rendering Systems
The heavy lifting is performed by parallel video rendering systems. In this architecture, distributed GPU workers pull jobs from the queue. Each worker is responsible for:
- Scene Assembly: Combining background assets, overlays, and dynamic text.
- AI Synthesis: Running TTS (Text-to-Speech), voice cloning, and lip-sync models.
- Compositing & Encoding: Using NVENC-accelerated FFmpeg to produce the final MP4 or WebM files.
By utilizing Kubernetes with a GPU operator, teams can autoscale node pools based on queue depth. If the queue exceeds 500 pending jobs, the system automatically spins up additional H100 or L40 instances to maintain a P95 render time of under 180 seconds per video.
Asset and Template Registries
An often-overlooked component of industrial scale AI video production is the template registry. This is a versioned repository of “video blueprints” that define variable schema contracts. For example, a “Summer Sale” template might require a customer_name (string), discount_percentage (int), and language_code (enum). By enforcing these contracts, you prevent runtime errors that could break a batch of 1,000 videos mid-render.
Source: TrueFan AI: Video Production Infrastructure for Enterprise Teams
2. MLOps: The Operational Backbone of Video Production
When scaling to 1,000 videos daily, you aren’t just managing files; you are managing models. This is where MLOps video production infrastructure becomes critical. In 2026, 78% of Indian enterprises have shifted from experimental AI to “GenAIOps” to ensure model reliability and output quality.
Model Registry and Rollout Policies
Your pipeline likely uses multiple models: one for the digital avatar, one for voice synthesis, and another for lip-syncing. A production-grade MLOps video production infrastructure requires a model registry with semantic versioning. Before a new lip-sync model is promoted to the “1,000/day” pipeline, it must pass a canary rollout. You might route 5% of traffic to the new model and monitor for “audio-visual drift”—a metric that measures the synchronization between phonemes and lip movements.
Data Pipelines for Personalization
Personalization at scale requires a “Feature Store” for video. For an India-focused growth team, this includes:
- Phonetic Dictionaries: Ensuring that regional names (e.g., “Aniruddha” or “Thiruvalluvar”) are pronounced correctly by the TTS engine. Explore voice cloning for Indian accents.
- Locale-Specific Assets: Automatically swapping a background image of a Mumbai skyline for a Chennai landmark based on the user’s IP or profile data.
Monitoring and Safety Gates
Scalable video ML operations India must account for content safety. Automated moderation layers must scan every rendered video for brand safety violations or “hallucinations” in the AI avatar’s expressions. If the safety pass rate drops below 99.8%, the pipeline should automatically trigger a revert to the previous stable model version. See guidance on brand guideline enforcement in AI.
Source: Tata Communications: MLOps to GenAIOps
3. CI/CD & DevOps: Treating Video as Code
To achieve industrial scale AI video production, you must treat your video templates and render configurations as code. This is the essence of CI/CD pipeline video creation.
GitOps for Video Templates
When a designer updates a video template (e.g., changing the CTA button color or font size), that change should be submitted as a Pull Request (PR). Automated DevOps automation video production scripts then run a “headless render” of a golden sample. If the new render deviates from the expected layout or exceeds the target file size for WhatsApp distribution, the build fails.
Automated Test Harnesses
Testing a batch of 1,000 videos manually is impossible. Instead, implement automated test harnesses that check:
- SSIM/PSNR Analysis: Comparing frames of the new render against a “golden” reference to detect visual artifacts.
- Phoneme Alignment: Ensuring the audio track matches the lip movements within a 20ms tolerance.
- Subtitle Timing: Verifying that burnt-in captions align perfectly with the spoken word, especially important for muted autoplay on social feeds.
Progressive Delivery
Using feature flags, you can roll out new video variants to specific segments of your audience. For instance, you might test a “High Energy” vs. “Professional” avatar persona. Studio by TrueFan AI’s 175+ language support and AI avatars make it easy to deploy these variants across diverse linguistic demographics in India without rewriting the core pipeline. Learn more about multimodal AI video creation.
Source: TrueFan AI: Batch Video Creation Automation
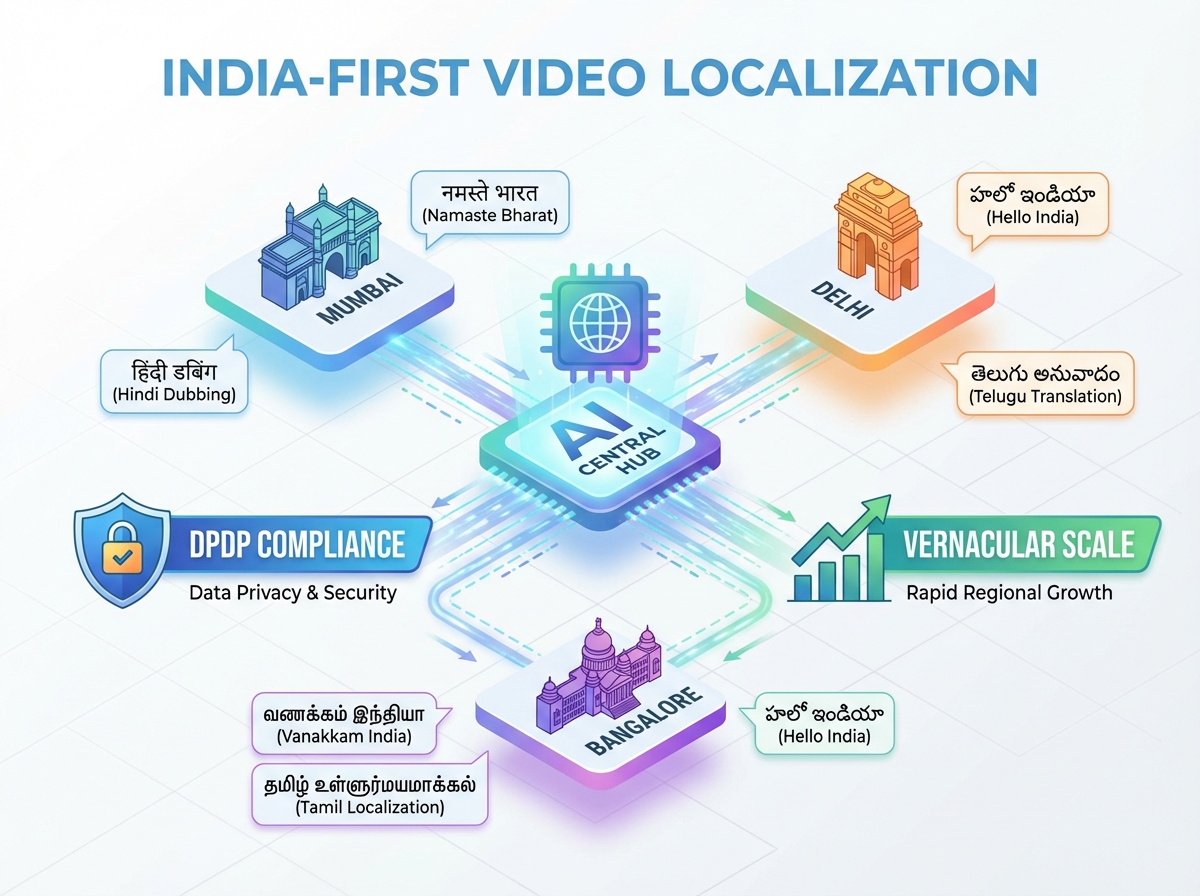
4. India-First Localization and DPDP Compliance
Operating a high-volume video generation workflow in India requires a deep understanding of the local regulatory and technical landscape. In 2026, compliance with the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act is non-negotiable for enterprise growth teams.
Vernacular Scale and Phonetic Correctness
India’s internet is vernacular-first. Data from 2026 shows that 62% of users in Tier 2 and 3 cities prefer video content in their mother tongue. Your bulk personalized video automation India strategy must support not just the major languages (Hindi, Tamil, Telugu) but also code-mixed “Hinglish” or “Tanglish” which often drives higher engagement in urban centers.
DPDP Compliance Framework
The DPDP Act 2023 mandates strict consent and purpose limitation. When generating 1,000 personalized videos daily, your infrastructure must:
- Log Consent: Maintain a tamper-proof audit trail of when and how a user consented to have their name or data used in a personalized video.
- On-Shore Processing: Use India-region GPU clusters (e.g., AWS Mumbai or Azure Central India) to ensure that sensitive PII (Personally Identifiable Information) does not leave the country.
- Right to Erasure: Implement automated workflows that delete a user’s personalized video assets from your CDN and storage buckets upon request.
Network and Device Realities
A 1080p video that looks great on a high-end iPhone might fail to load on a budget device in a low-bandwidth area. Your enterprise batch video infrastructure should automatically generate “bitrate ladders”—multiple versions of the same video (240p, 480p, 720p) optimized for WhatsApp’s compression algorithms and varying network speeds. See this optimization guide.
Source: MeitY: Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
5. Performance Engineering and Cost Optimization
The unit economics of enterprise video batch processing 1000 daily can make or break a campaign. Without optimization, GPU costs can spiral.
GPU Utilization and Spot Instances
To reduce costs, implement a hybrid GPU strategy. Use “On-Demand” instances for critical, real-time renders and “Spot” instances for large-scale batch processing. By 2026, advanced orchestration tools allow for “checkpointing” in video rendering—if a Spot instance is reclaimed by the provider, the job can resume from the last rendered frame on a new instance, preventing wasted compute.
| Metric | On-Demand (H100) | Spot (H100) | Savings % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost per Render Minute | ₹85.00 | ₹28.00 | 67% |
| Availability | 99.9% | Variable | - |
| Best Use Case | Real-time API calls | Batch 1000+ daily | - |
Caching and Asset Reuse
In a batch of 1,000 videos, often 80% of the visual content (the background, the brand logo, the outro) is identical. Intelligent parallel video rendering systems cache these intermediate frames. Instead of re-rendering the entire 30-second clip, the system only renders the “dynamic” portions (the avatar’s face and lips) and composites them onto the cached background, reducing render time by up to 60%.
Throughput Planning
To hit the 1,000/day target, you need a capacity model. If one video takes 3 minutes to render on a single GPU, you need approximately 3,000 minutes of GPU time per day. Spreading this across 10 parallel workers reduces the total wall-clock time to just 5 hours, allowing for multiple batch runs per day to accommodate A/B testing cycles.
Source: Rapyder: MLOps Services in India
6. Measurement, Experimentation, and the Build vs. Buy Decision
The ultimate goal of automated A/B testing videos scale is to find the “winning” creative that drives down Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC). Solutions like Studio by TrueFan AI demonstrate ROI through their ability to rapidly iterate on these variants without requiring a massive in-house engineering team.
Automated A/B Testing at Scale
With a 1,000-video-per-day capacity, you can test dozens of variables simultaneously. Explore YouTube Shorts automation for inspiration:
- Avatar Persona: Does a younger avatar perform better for fintech ads?
- Hook Timing: Does mentioning the offer in the first 3 seconds increase CTR?
- Language Nuance: Does “Hinglish” outperform pure Hindi in Delhi-NCR?
By 2026, performance marketing teams are using “Multi-Armed Bandit” algorithms to automatically shift budget toward the video variants that are showing the highest conversion rates in real-time.
Build vs. Buy: The Strategic Choice
Building a custom enterprise batch video infrastructure from scratch offers maximum flexibility but comes with high “undifferentiated heavy lifting.”
- Build: If you have a highly proprietary rendering engine or extreme infosec requirements that necessitate a completely air-gapped environment.
- Buy/Partner: If you need to hit the market in under 30 days with enterprise-grade governance, ISO 27001 certification, and India-ready localization.
For most growth teams, a hybrid approach is best: use a robust platform like Studio by TrueFan AI for the core rendering and avatar synthesis, while building custom orchestration on top of their APIs to handle your specific business logic and data integrations.
Implementation Roadmap: 30/60/90 Days
Day 0–30: The Foundation
- Set up your orchestration layer and template registry.
- Integrate with an API-driven rendering service.
- Establish “Golden Tests” for your first 5 templates.
- Goal: Render 50 videos/day with 100% manual QA pass.
Day 31–60: Hardening and Automation
- Implement CI/CD pipeline video creation for template updates.
- Add automated moderation and DPDP consent logging.
- Expand to 10+ regional languages.
- Goal: Achieve 500 videos/day with automated QA.
Day 61–90: Industrial Scale
- Optimize costs using Spot instances and frame caching.
- Launch automated A/B testing videos scale with real-time performance feedback.
- Scale to 1,000+ videos/day across all major Indian vernaculars.
- Goal: Full production at 1,000+/day with a 65% reduction in cost-per-video.
Sources:
- TrueFan AI: Video Production Infrastructure for Enterprise Teams
- MeitY: Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023
- Tata Communications: MLOps to GenAIOps
- SAS: GenAI ROI Study 2025/26
- Kantar: Marketing Trends 2026
Conclusion
By following this playbook, growth teams can transform video from a bottlenecked creative process into a scalable, data-driven engine. The future of performance marketing in India is personalized, vernacular, and—most importantly—automated.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ: Scaling Enterprise Video Infrastructure
What does “enterprise video batch processing 1000 daily” practically require?
It requires a distributed architecture where rendering is decoupled from the application logic. You need a GPU pool (typically 10–15 L4 or T4 equivalent GPUs), a robust job queue (like Celery or SQS), and a CI/CD pipeline to validate templates before they hit production. Most importantly, you need an SLA-driven approach where P95 render times are monitored to ensure campaign deadlines are met.
How do “parallel video rendering systems” avoid bottlenecks?
Bottlenecks are avoided through “sharding” and “warm pools.” By sharding jobs by template ID, you can keep the necessary AI models “warm” in GPU memory, avoiding the 30–60 second cold-start latency of loading a new model for every video. Additionally, queue-depth-based autoscaling ensures that as your batch size grows, your compute capacity grows with it.
How is “CI/CD pipeline video creation” tested?
Testing involves three layers: (1) Schema Validation: Ensuring the input data (CSV/API) matches the template requirements. (2) Visual Regression: Using AI to compare the rendered output against “golden frames” to ensure no UI elements are overlapping. (3) Linguistic QA: Automated checks to ensure the TTS output matches the intended script without pronunciation errors.
How to ensure DPDP compliance in “bulk personalized video automation India”?
Compliance is achieved by implementing “Privacy by Design.” This includes encrypting all PII at rest, using India-based data centers for processing, and maintaining a “Consent Registry” that links every generated video to a specific user consent token. Studio by TrueFan AI simplifies this by offering a “walled garden” approach with built-in moderation and compliance logs that align with Indian regulatory standards.
What KPIs drive “automated A/B testing videos scale”?
Beyond traditional CTR and CVR, you should track: Variant Coverage (the percentage of your audience receiving a personalized variant), Render Success Rate (the percentage of jobs that complete without errors), and Creative Fatigue Index (how quickly a specific video variant’s performance declines, triggering an automated request for a new batch of variants).




